What are Electroceuticals®?
Electroceuticals® are electronic devices designed to affect biological systems in such a fashion as to alleviate or mitigate symptomatology and/or pathology; or
An electric/electromagnetic therapy designed to affect biological systems in such a fashion as to alleviate or mitigate symptomatology and/or pathology.
Our non-invasive, wearable medical devices are designed to deliver our proprietary Electroceutical® Therapy using induction via the application of pulsed radio-frequency (PRF) waves at 27.12 MHz.
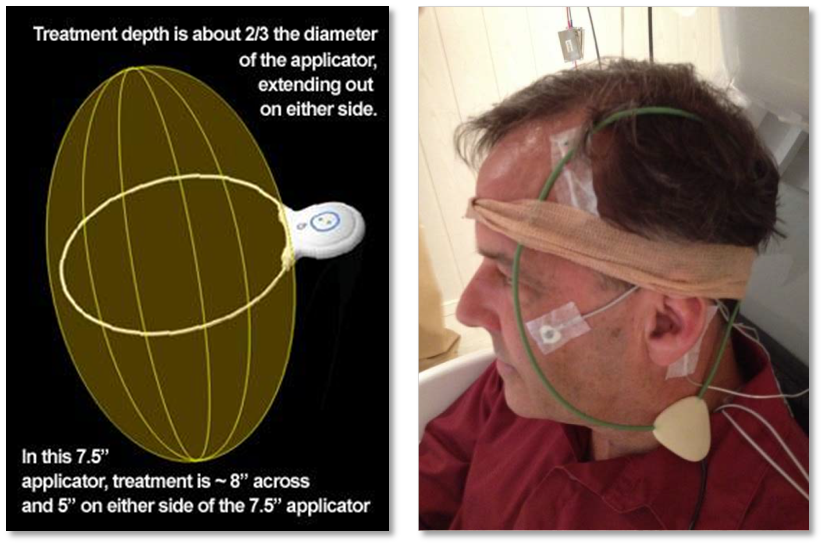
How Our Non-Invasive Electroceutical® Therapies Work:
Pulsed Electromagnetic Field-based (PEMF) Electroceuticals® which use a changing electromagnetic field to deliver electrical stimulation to tissues via induction function by accelerating the production of the endogenous constitutive nitric oxide synthesis systems (cNOS or eNOS): the anti-inflammatory system.
Nitric oxide (NO) is an essential molecule involved in several physiological and pathological processes within the mammalian body. NO is synthesized by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) which oxidizes a guanidine nitrogen of L-arginine releasing nitric oxide in the form of a free radical and citrulline.
Three isoforms of the NOS have been identified: endothelial (eNOS or NOS-3), neuronal (nNOS or NOS-1), and inducible (iNOS or NOS-2) – each with separate functions. The neuronal enzyme (NOS-1) and the endothelial isoform (NOS-3) are calcium-dependent and produce low levels of gas as a cell signaling molecule. The inducible isoform (NOS-2) is calcium independent and produces large amounts of gas which can be cytotoxic.
Nitric oxide thus generated acts as a messenger in diverse functions including vasodilation neurotransmission, anti-tumor and anti-pathogenic activities. Sufficient levels of NO production are necessary in protecting an organ such as the heart, brain, or liver from ischemic damage. NO dilates blood vessels, raising blood supply and lowering blood pressure. Nitric Oxide is also an immune effector, producing an anti-inflammatory effect at physiological levels.
In 1992, for its importance in neuroscience, physiology, and immunology, nitric oxide was proclaimed the “Molecule of the Year”. The 1998 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine was awarded for discovering nitric oxide’s role as a cardiovascular signalling molecule. Over a century after their medical introduction, the organic-nitrate pharmaceuticals, including nitroglycerine and amyl nitrite, were identified as precursors of nitric oxide.
